60SG
Holry
| MOTOR SIZE: | |
|---|---|
| Screw Specifications: | |
| Availability: | |
| Quantity: | |
Product Description
The HOLRY' brand of hybrid Stepper Motor Linear Actuators come in five sizes, from 28 mm square to 86 mm square, corresponding to Nema size 11, size 14, size 17, size 23, and size 34. Each size has three to three form factors available - captive, non-captive and an external linear version.
There are over twenty different travels per step available, from. 0001563 inch (.00397 mm) to .003937 inch (1 mm). Microstepping can be used for even finer resolution.
The NEMA 24 Stepper Motor has an integrated 15 cm (5.9″) threaded rod as its output shaft, turning it into a linear actuator capable of precision open loop positioning.
The "24" in NEMA 24 indicates its size, which means it has a frame size of 2.4 inches (60 mm) square.This standardized sizing system helps ensure compatibility with mounting brackets and other hardware.
Features
Much easier to integrate into an application; can be coupled with programmable controllers/drivers.
Provide higher level of precision in motion control (speed, torque and force can be modified at different stages during movement).
Actuators are not susceptible to leakages or contamination - safer, cleaner and more convenient.
More economical in the long run, require less maintenance, are rugged and easy to operate / install, last longer and can be reliably used in different environmental conditions.
With simple quick connect wires and cable, actuators can be easily assembled, are more compact, and operate quietly.
The "24" in NEMA 24 indicates its size, which means it has a frame size of 2.4 inches (60 mm) square.This standardized sizing system helps ensure compatibility with mounting brackets and other hardware.
Stepper motors move in discrete steps, and the stepping angle of a NEMA 24 motor is typically 1.8 degrees per step.This means it rotates 1.8 degrees with each step, making it suitable for applications requiring precise control and positioning.
NEMA 24 motors come in various models with different holding torque ratings.Holding torque is the amount of torque the motor can exert to maintain its position when stationary.The specific holding torque depends on the motor's design and specifications.
The voltage and current requirements of a NEMA 24 motor can vary depending on the model and application.It's important to provide the motor with the correct voltage and current to ensure proper performance.
NEMA 24 stepper motors typically have four or six wires, which are used to control the motor. Proper wiring and connection to a stepper motor driver or controller are essential for its operation.
NEMA 24 motors have a standardized mounting pattern, which makes it easier to attach them to various equipment and machinery.The mounting holes are typically positioned at specific distances and locations on the motor's frame.
NEMA 24 stepper motors are commonly used in applications that require precise control of rotational motion, such as in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines for cutting and milling, 3D printers for layer-by-layer printing, and robotic systems for accurate positioning.
To operate a NEMA 24 stepper motor, you'll need a stepper motor driver or controller.These devices provide the necessary electrical pulses to control the motor's rotation and direction.
Some stepper motor drivers support microstepping, which allows for even finer control of the motor's position by subdividing each step into smaller increments.This can improve the motor's overall performance, especially in applications where smooth motion is essential.
Configurations
Kindly check our stepper motor catalog for full specifications.
 Holry Stepper Motor Catalogue.pdf
Holry Stepper Motor Catalogue.pdf
The key differences between an external linear, non-captive, and captive motor is,
External | Non-captive | Captive |
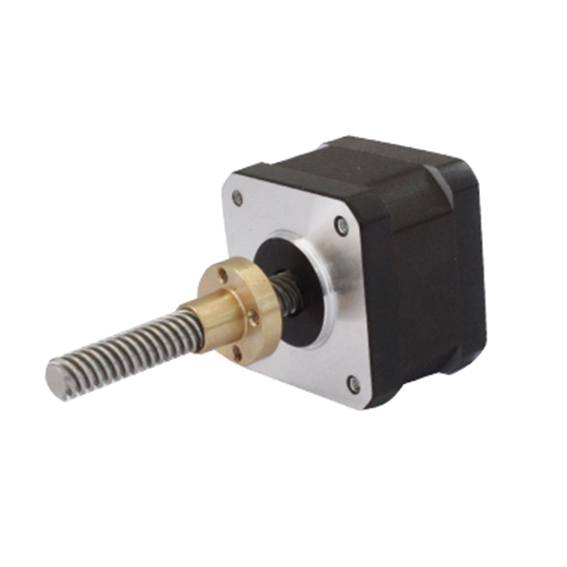  |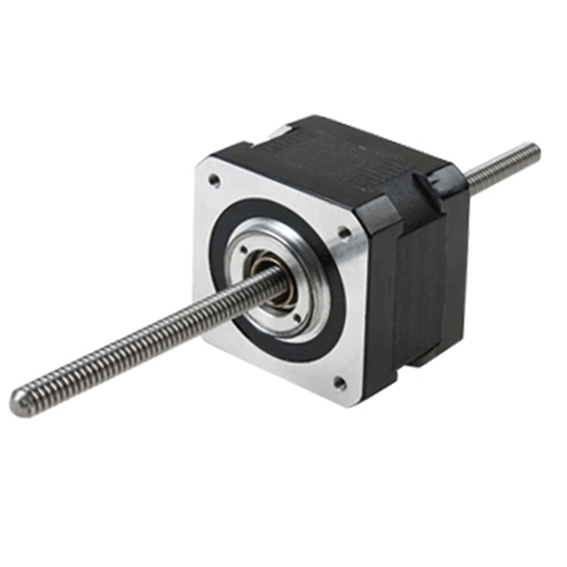   | 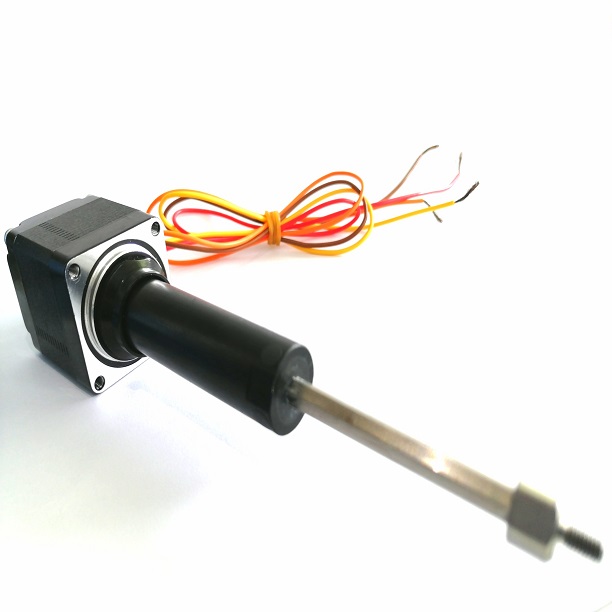  |
| The external linear motor has the screw affixed to the rotor, so it rotates external to motor body, like a DC motor. | The non captive screw travels freely in and out of the motor body and does not rotate. | The captive has a short screw that is held mostly inside the motor body, coupled to a spline. |
| External linear motors are most akin to motorized rails where the nut is replaced by a driven carriage assembly. Non captive is generally the shortest overall length assembly, while the captive is the longest. | ||
End Machine Options | Screw Nut Options |
 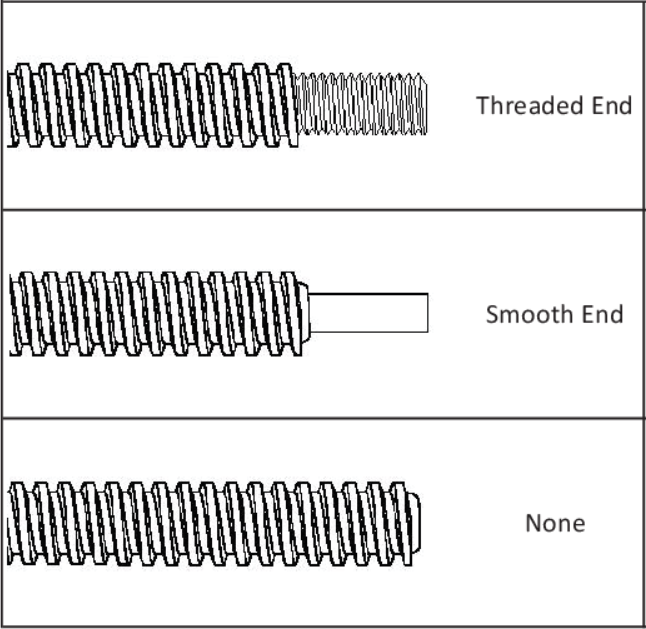 |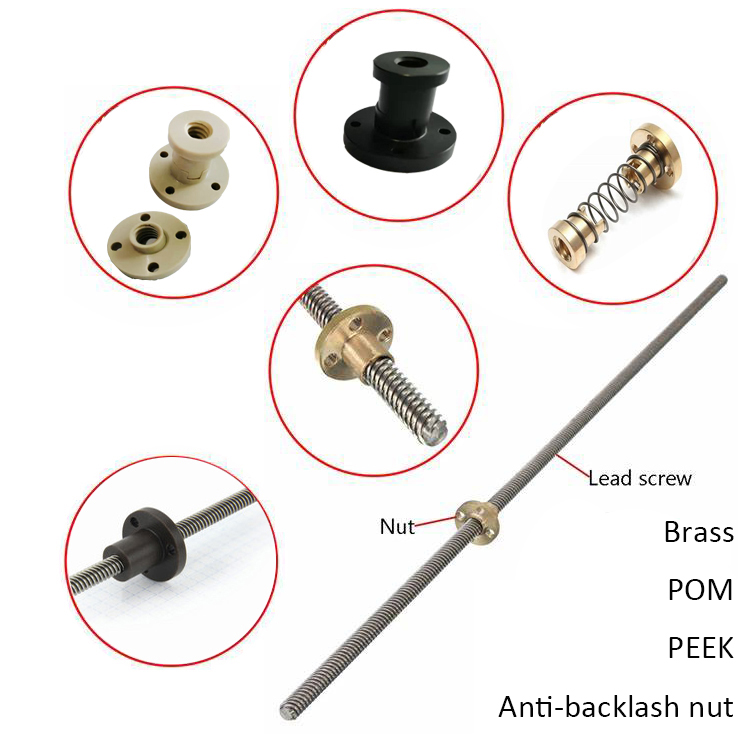   |
| Please contact HOLRY for custom solutions. | |
Appilcations

NEMA 24 stepper motors find a wide range of applications across various industries due to their precise control of rotational motion and versatility. Here are some common applications for NEMA 24 stepper motors:
CNC Machinery
NEMA 24 stepper motors are frequently used in computer numerical control (CNC) machines, including milling machines, lathes, and routers. They provide the precise control required for accurately positioning the cutting tools or workpieces.
3D Printing
In 3D printers, NEMA 24 motors are used to control the movement of print heads, build platforms, and other components. Their ability to move in precise increments is essential for creating intricate 3D-printed objects.
Robotics
NEMA 24 stepper motors play a crucial role in various robotic systems, including robotic arms, pick-and-place machines, and automated assembly lines. Their ability to move with precision and reliability is vital for robotic motion control.
Textile Machinery
In the textile industry, NEMA 24 stepper motors are used in machines like sewing machines, embroidery machines, and fabric cutters. They enable precise control of thread tension, needle movement, and fabric feeding.
Medical Devices
Stepper motors are found in medical equipment such as laboratory automation systems, medical imaging devices, and robotic surgical instruments. Their accuracy and reliability are essential for delicate medical procedures.
Laboratory Automation
NEMA 24 stepper motors are used in laboratory automation equipment for tasks like liquid handling, sample processing, and automated testing. They ensure precise and repeatable movements.
Aerospace
In aerospace applications, stepper motors can be found in systems like satellite dish positioning, antenna control, and automated inspection equipment. Their ability to operate in harsh environments and maintain accuracy is critical.
Automated Packaging
Stepper motors are used in packaging machinery to control processes like filling, sealing, labeling, and sorting. They ensure consistent and reliable packaging of products.
Automotive Manufacturing
NEMA 24 stepper motors are used in automotive manufacturing for tasks such as welding, painting, and assembly line automation. They help ensure the precision and quality of automotive components.
Camera and Photography Equipment
In professional photography and filmmaking equipment, stepper motors are used to control features like focus and zoom in camera lenses, as well as camera rig movements.
Telescope Mounts
In amateur and professional telescopes, stepper motors are used to control the movement of the telescope mount, allowing astronomers to track celestial objects accurately.
Industrial Automation
NEMA 24 stepper motors are employed in various industrial automation applications, including conveyor systems, material handling, and automated testing and inspection equipment.
These are just a few examples of how NEMA 24 stepper motors are utilized in different industries and applications. Their ability to provide precise control, repeatable motion, and reliability makes them a popular choice for a wide range of tasks that require accurate positioning and automation.
FAQ
The stepper motor is an electromagnetic device that converts digital pulses into mechanical shaft rotation. Advantages of step motors are low cost, high reliability, high torque at low speeds and a simple, rugged construction that operates in almost any environment.
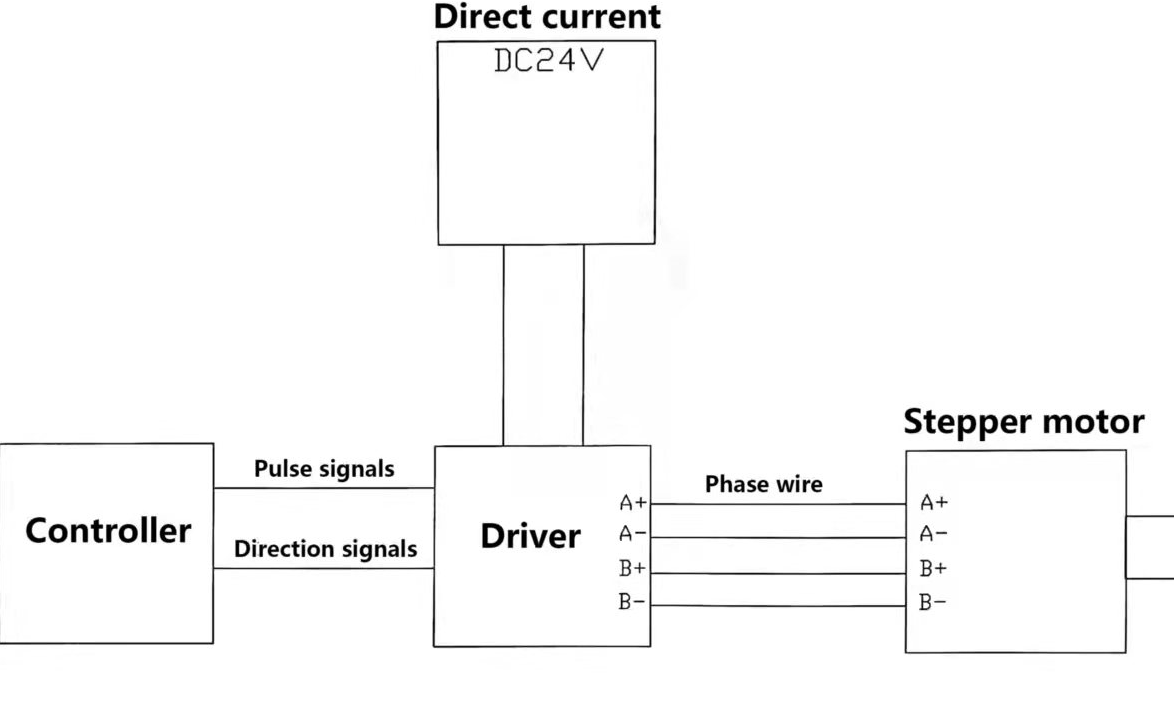
Stepper motors are so named because each pulse of electricity turns the motor one step. Stepper motors are controlled by a driver, which sends the pulses into the motor causing it to turn.
Step angle is defined as the angle through which the stepper motor shaft rotates for each command pulse.
If external force is applied to a stepping motor when it is stopped but energized, the attractive force generated between the rotor and stator works to maintain the stop position of the motor. This torque of withstanding the external force is called the holding torque.