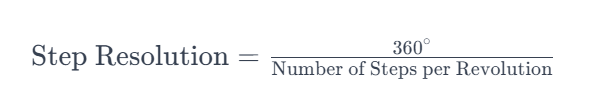-
Q How do I troubleshoot common issues with stepper motors?
A Check for loose connections, verify power supply compatibility, inspect wiring for correct polarity, and ensure there are no mechanical obstructions. Reviewing controller settings and testing with an alternate controller or driver can help identify and resolve issues.
-
Q Do stepper motors require feedback for position control?
A While stepper motors can operate in an open-loop system without feedback, closed-loop systems with feedback devices like encoders or sensors are used in applications where precise position control and error correction are essential.
-
Q What is microstepping, and how does it improve stepper motor performance?
A Microstepping is a technique that divides each full step of a stepper motor into smaller sub-steps. This allows for smoother motion, reduced vibration, and improved positioning accuracy, especially at low speeds.
-
Q What is the significance of step angle in stepper motors?
A Step angle is the angle through which the motor rotates for each input pulse. It is a critical parameter that determines the motor's resolution and accuracy. Smaller step angles result in finer control but may require more complex drive electronics.
-
Q What are the key components of a stepper motor system?
A A stepper motor system consists of the stepper motor itself, a driver to control the motor, and a controller or microcontroller that generates the sequence of pulses to drive the motor.
-
Q What is a stepper motor, and how does it differ from other types of motors?
A A stepper motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical pulses into precise mechanical movements. Unlike other motors, it moves in discrete steps, allowing for accurate control of position and speed.
-
Q Can stepper motors operate in an open-loop configuration?
A Yes, stepper motors can operate in an open-loop system, where position control is achieved without external feedback devices. However, for critical applications, closed-loop systems with feedback may be preferred to enhance accuracy and correct errors.
-
Q What is microstepping, and why is it important?
A Microstepping is a technique that divides each full step of a stepper motor into smaller increments. This provides smoother motion, reduces vibration, and improves accuracy. Microstepping is essential for applications demanding precision.
-
Q How is the step resolution of a stepper motor determined?
A Step resolution is the smallest angle the motor can move in response to a single input pulse. It is determined by the motor's construction, the number of poles, and the drive electronics. Higher pole counts and microstepping can enhance resolution.
To calculate the step resolution, you can use the following formula:
-
Q What are the advantages of using stepper motors?
A Stepper motors offer precise control of movement, high torque at low speeds, simplicity of control, and open-loop operation (no feedback required). They are ideal for applications requiring accurate position control.
-
Q What is a stepper motor, and how does it work?
A Here's a breakdown of how a stepper motor works:
Construction:
A typical stepper motor comprises a rotor and a stator. The rotor is the rotating part, while the stator is the stationary part. The rotor is usually equipped with teeth or a magnetic structure that interacts with the magnetic fields generated by the stator.
Stator and Windings:
The stator contains coils of wire wound around poles. These coils are energized sequentially to create a rotating magnetic field. The number of poles and windings in the motor determines its step angle, which is the angle through which the motor rotates for each input pulse.
Magnetic Interaction:
When an electric current is applied to a coil in the stator, it generates a magnetic field. The rotor, which is typically made of a permanent magnet or ferromagnetic material, aligns itself with the magnetic field created by the energized stator coil. This causes the rotor to move to a specific position.
Step Rotation:
Stepper motors move in discrete steps, and the angle of rotation for each step is determined by the motor's design. The sequence of energizing the stator coils dictates the direction and distance of each step. By controlling the sequence of these pulses, precise control over the motor's position and speed is achieved.
Control Signals:
To operate a stepper motor, a controller or microcontroller sends a series of electrical pulses to the motor's stator windings. The order and timing of these pulses determine the direction and speed of the motor. This control method allows for accurate positioning without the need for external sensors.
Full-Step and Microstepping:
Stepper motors can operate in full-step mode, where each pulse corresponds to a single step. Alternatively, microstepping subdivides each step into smaller increments, providing smoother motion and finer resolution. Microstepping is achieved by controlling the current in the motor's coils more precisely.
-
Q How do you use a motor driver?
A We use motor drivers to give high power to the motor by using a small voltage signal from a microcontroller or a control system. If the microprocessor transmits a HIGH input to the motor driver, The driver will rotate the motor in one direction keeping the one pin as HIGH and one pin as LOW.
-
Q What is motor and motor drive?
A A motor is the mechanical or electrical device that generates the rotational or linear force used to power a machine. A drive is the electronic device that harnesses and controls the electrical energy sent to the motor. It is important to distinguish between motors and drives.
-
Q Why should you buy from us not from other suppliers?
A Products conform to CE and ROHS standards, and have a good reputation at home and abroad. The company has a group of excellent, experienced management and technical personnel.
-
Q How do DC motor drivers work?
A A DC motor controller manipulates the position, speed, or torque of a DC-powered motor and easily reverses, so the DC motor drive current runs in the opposite direction. Enjoy higher starting torque, quick starting and stopping, reversing, variable speeds with voltage input and more.
-
Q What is a motor driver?
A The output form of the motor driver is output in digital form, so the PWM pulse modulator is used to control the speed of the motor, and the movement and direction of the motor are controlled by the current.
-
Q What is the main reason to use a stepper motor?
A Essentially, stepper motors provide excellent speed control, precise positioning, and repeatability of motion. Also, stepper motors are very reliable because there are no contact brushes in the motor. This minimizes mechanical failure and maximizes the life of the motor. Moreover, stepper motors are more affordable than other motors and have a wide range of applications.
-
Q Why are stepper motors important?
A Stepper motors can produce full, instantaneous torque - even from a standstill. This makes them very useful for motion control applications, where accuracy, repeatability, and power are paramount.
-
Q What is stepper motor explanation?
A Stepper motors are DC motors that move in discrete steps. They have multiple coils that are organized in groups called "phases". By energizing each phase in sequence, the motor will rotate, one step at a time. With a computer controlled stepping you can achieve very precise positioning and/or speed control.
-
Q Why use gear reducer?
A Speed reducers, also called gear reducers, are mechanical gadgets by and large utilized for two purposes. Gear reducers essential use is to duplicate the measure of torque produced by an information power source to expand the measure of usable work.
English
Русский
العربية
Français
Español
Português
Deutsch
italiano
日本語
한국어
Nederlands
Tiếng Việt
ไทย
Polski
Türkçe
አማርኛ
Bahasa Melayu
தமிழ்
Filipino
Bahasa Indonesia
magyar
Română
Čeština
हिन्दी
فارسی
Kiswahili
Slovenčina
Slovenščina
Norsk
Svenska
українська
Ελληνικά
Suomi
עברית
Dansk
বাংলা
Hrvatski
Afrikaans
Gaeilge
Eesti keel
Māori
සිංහල
Azərbaycan dili
Euskara
Беларуская мова
Български
guarani
Kreyòl ayisyen
Kurdî
Lietuvių
Македонски
తెలుగు